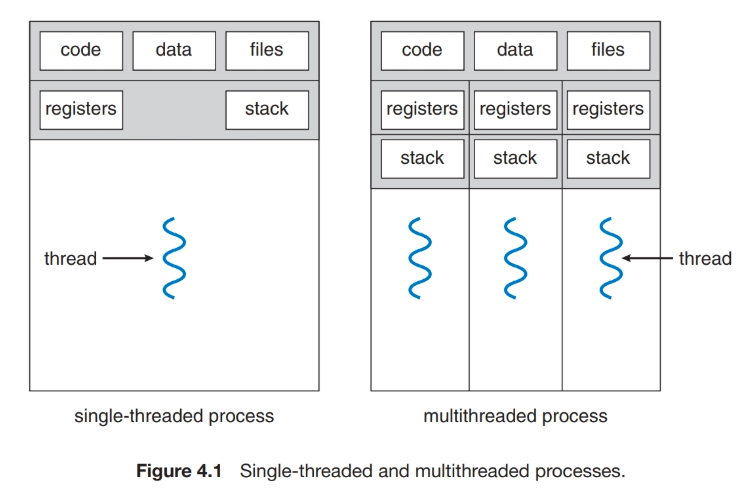
Operating System Thread
Thread
A fundamental unit of CPU utilization
Those are have to be added to PCB
- It has to have own thread ID
- Keep track program counter
- Have to own register set
- Stack(Have to know where i was)
What has to be shared?
- code section
- data section
- other OS resources
- file handles
- signal..
- 2^N (Formula for the process created when N is indicating loop number)
- for(i = 0 i<4; i++) means 2^4 = 16 processes are created
- 2^N-1 (Formula for the # of child processes)
Benefits - Responseiveness - Resource sharing - Economy - Scalability
Multicore Programming
- multicore(On same ship) / multi processor
- each appears as separate processor to OS
Parallelism / Concurrency
- Parallel system : More then 1 task at same time
-
Concurrent system : All task’s make “progress”
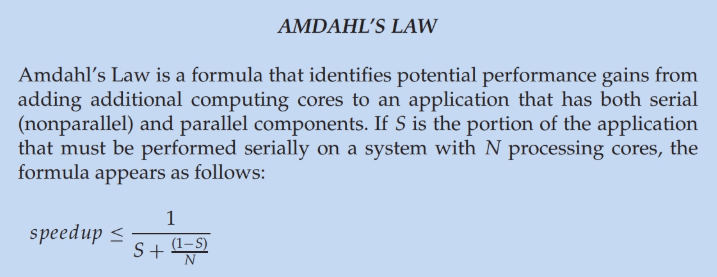
- Hardware support increasing for multiple cores 2, 4, 8
Programming Challenges(multicore)
- Ident: fying Tasks
- How do we break up a process
- Balance
- How to distribute tasks across cores
- Data splitting
- How to place data[where physically]
- Data dependency
- Managing data shared by tasks
- Testing and debugging
- Concurrency add big increase in complexity
Types of Parallelism
- Data
- Task
- Data Parallelism
- distribution of subsets of same data across multiple cores and then performing the same operation on each.
- same function
- Task Parallelism
- different function
- distribution of tasks(threads) across multiple cores. Each task is performing a unique operation
- same data
- Most common to have a hybrid approach as location of data can have by impact on task performance
Example
- 6 cores mean 6 processors
- 6 threads mean could be one hardware threads or six hardware threads.
MultiThread Models
- User Threads(User application simulating multithread, No support from kernel)
- Kernel Threads(Management and support from the kernel)
- One-To-One Model - kernel threads
- Many-To-One Model - user threads (many user -> 1 kernel)
- Many-To-Many
Thread Libraries
- User an API for management Thread
Thread Pool
Thread Issues
- Creation
- Signal Handling
- Goes to specific thread
- A signal is generated by the occurrence of a particular event
- The signal is delivered to a process
- Once delivered, the signal must be handled
Thread Cancellation
- Asynchronous cancellation
- One thread immediately terminates the target thread
- Deferred cancellation
- The target thread periodically checks whether it should terminate, allowing it an opportunity to terminate itself in an orderly fashion.